1. About Methylpropiophenone
1.1 What is Methylpropiophenone?
Methylpropiophenone, a significant chemical compound, is characterized by its unique molecular structure and versatile properties. This aromatic ketone plays a pivotal role in various industrial applications, making it a subject of interest for researchers and professionals alike. Known for its distinct aromatic properties, Methylpropiophenone is often a key component in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals.
1.2 What is Methylpropiophenone used for?
Methylpropiophenone finds widespread use in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, contributing to the development of essential drugs. Its versatile nature allows it to be employed in agrochemical formulations, helping enhance crop yields and protect plants from pests. Additionally, this compound plays a crucial role in the production of specialty chemicals, showcasing its significance across various industries.
2. Methylpropiophenone and 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone
2.1 Relationship
To convert Methylpropiophenone to 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone, perform a bromination reaction. Mix Methylpropiophenone with bromine in the presence of a suitable solvent. The bromine selectively adds to the Methylpropiophenone molecule, replacing a hydrogen atom with a bromine atom. Isolate the product through appropriate workup procedures, which may involve quenching excess bromine and purification steps. Always follow safety protocols when working with reactive chemicals like bromine.
Chemical Equation:
CH3COC6H5 + Br2 → CH3COBrC6H4Br
2.2 What is 2 Bromo 4 ‘- Methylpropiophenone?
2-Bromo-4′-Methylpropiophenone CAS 1451-82-7 is a key derivative with distinct chemical characteristics. The bromination at a specific position alters the compound’s chemical behavior, making it suitable for specialized applications. Researchers often leverage this derivative for its unique reactivity in various chemical reactions.
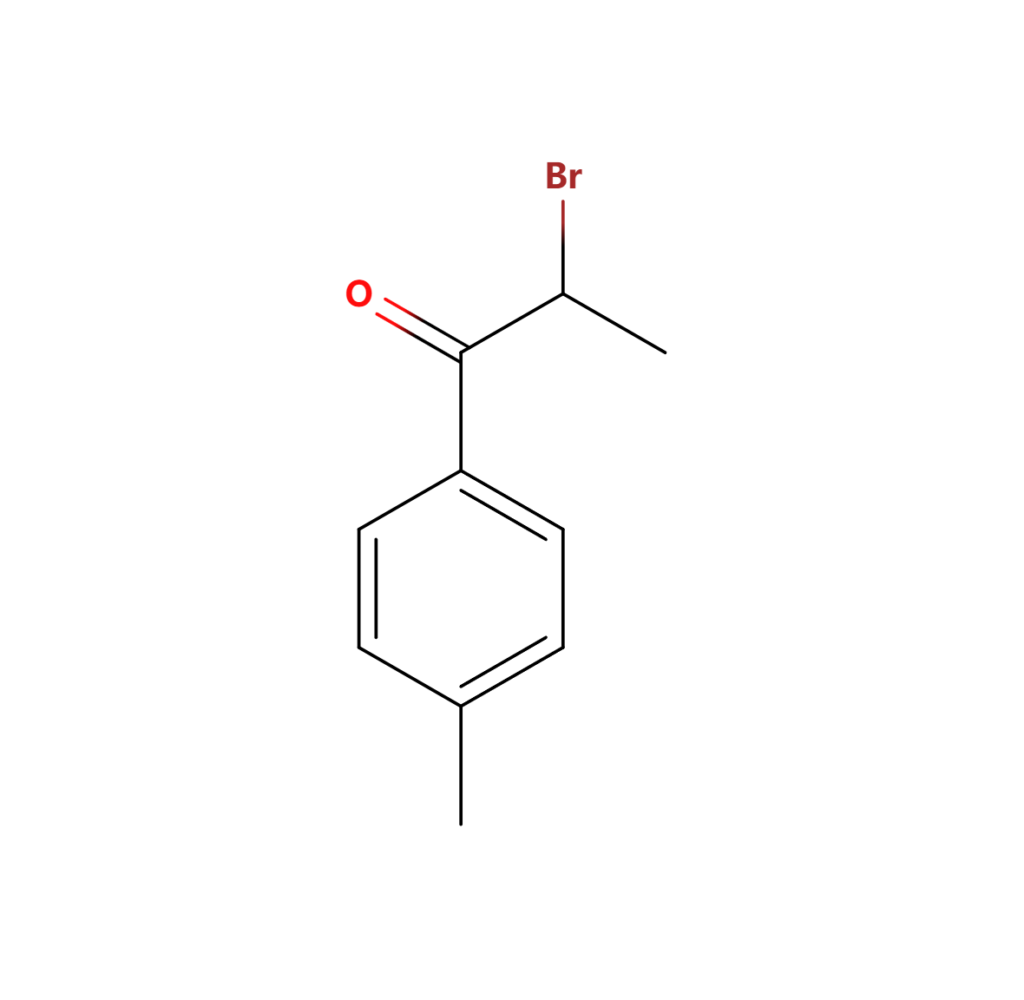
2.3 What is 2 Bromo 4 Methylpropiophenone used for?
The applications of 2-Bromo-4-Methylpropiophenone extend across various industries, including pharmaceuticals and chemical synthesis. Its enhanced reactivity makes it a preferred choice for specific reactions, facilitating the production of compounds that might be challenging to obtain using the parent Methylpropiophenone. Industries involved in drug discovery and development particularly benefit from the unique properties of this derivative.
2.4 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone Buy Online
JHchemco specializes in supplying fine chemical raw materials globally, including 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone, 2-bromo-3-methylpropiophenone, and 4′-methylpropiophenone. We offer door-to-door shipping, 7-14 days fast delivery. We have warehouses in the US, Canada, Russia, Australia, Europe, etc.
3. Methylpropiophenone and 2-bromo-3-methylpropiophenone
3.1 Relationship
To convert Methylpropiophenone to 2-bromo-3-methylpropiophenone, you can perform a bromination reaction by mixing Methylpropiophenone with bromine in a suitable solvent. This reaction introduces a bromine atom selectively at a specific position in the Methylpropiophenone molecule, forming 2-bromo-3-methylpropiophenone as the product. The mixture is then processed to isolate and purify the final compound.
Chemical Equation:
CH3COC6H5 + Br2 → CH3COC6H4Br-3
3.2 What is 2 Bromo 3 Methylpropiophenone used for?
The unique properties of 2-Bromo-3-Methylpropiophenone CAS 1451-83-8 make it suitable for specific applications. This derivative’s distinct reactivity opens up possibilities for new synthetic routes, enabling the creation of compounds with tailored properties. Industries involved in material science and custom synthesis often find value in incorporating this derivative into their processes.
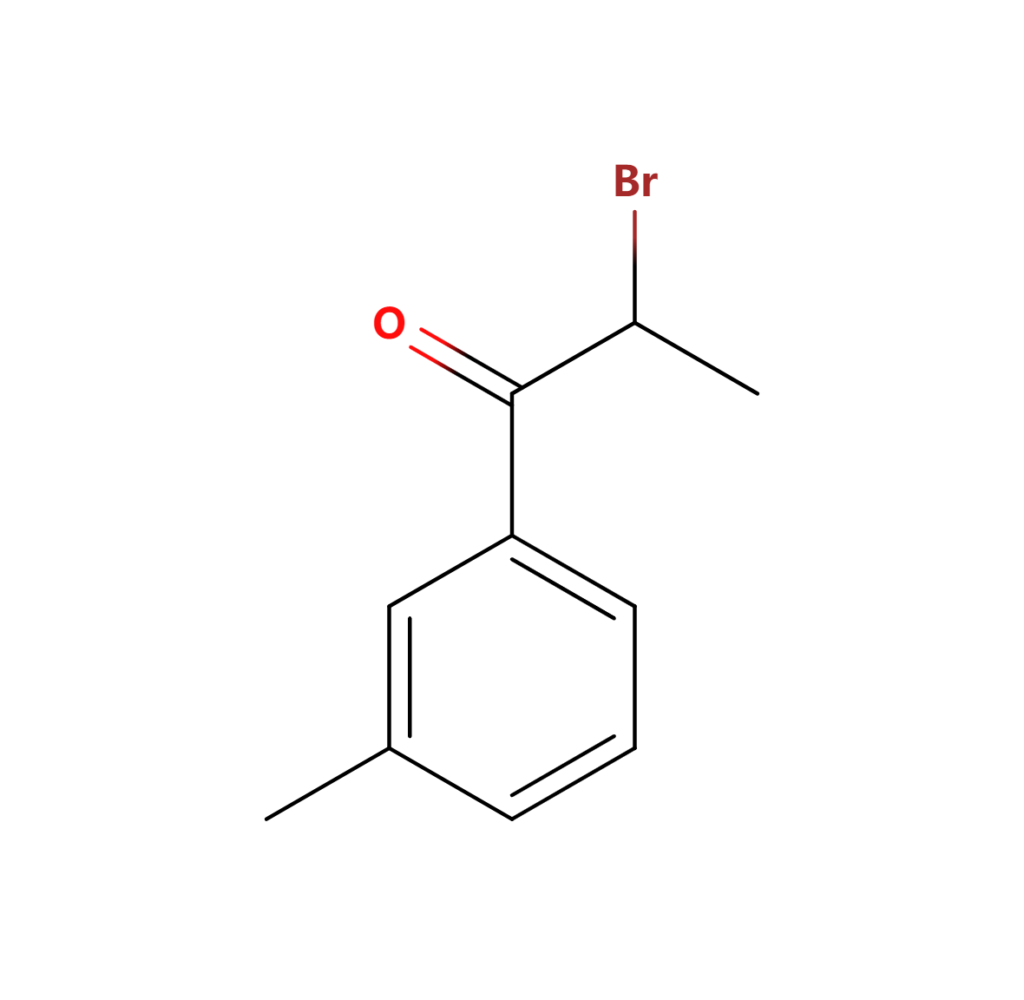
4. Methylpropiophenone and 4’-Methylpropiophenone
4.1 Relationship
The conversion of Methylpropiophenone to 4-methylpropiophenone involves a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, where Methylpropiophenone reacts with a methylating agent in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst. The chemical equation for this reaction is as follows: C9H10O + CH3I + AlCl3 → C9H9OCH3 + HCl
In this equation, Methylpropiophenone (C9H10O) reacts with methyl iodide (CH3I) in the presence of aluminum chloride (AlCl3), resulting in the formation of 4-methylpropiophenone (C9H9OCH3) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) as a byproduct.
4.2 What is 4 Methylpropiophenone used for?
Delving into the applications of 4-Methylpropiophenone CAS 5337-93-9 highlights its role in different industrial processes. The additional methyl group influences the compound’s solubility, melting point, and reactivity, making it suitable for specific reactions and industries. Understanding its uses contributes to the overall comprehension of this compound’s significance in the realm of fine chemicals and custom synthesis.
4.3 What is methylpropiophenone cas 5337 93 9?
Methylpropiophenone, with the CAS number 5337-93-9, holds a unique identification in chemical databases. This alphanumeric code serves as a vital reference for researchers, scientists, and professionals working with this compound. The CAS number ensures accurate and standardized identification, streamlining communication and documentation within the scientific community.

5. Difference between the Three Compounds
The compounds with CAS numbers 1451-82-7 (2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone), 1451-83-8 (2 Bromo 3 Methylpropiophenone), and 5337-93-9 (4’-Methylpropiophenone) are distinct chemical entities with variations in their molecular structures, which result in differences in their properties and applications. Let’s explore the key differences between these three compounds:
5.1 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone (CAS: 1451-82-7)
- Chemical Structure: This compound is derived from Methylpropiophenone by the introduction of a bromine atom at a specific position in the molecular structure.
- Applications: It is commonly used in chemical synthesis, especially in pharmaceutical and agrochemical research. The bromine substitution enhances its reactivity, making it valuable in certain reactions.
5.2 2 Bromo 3 Methylpropiophenone (CAS: 1451-83-8)
- Chemical Structure: This compound is another derivative of Methylpropiophenone, where bromine is introduced at a different position compared to 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone.
- Applications: The unique placement of the bromine atom imparts distinct properties, potentially making it suitable for specific reactions or applications in fields like material science and custom synthesis.
5.3 4’-Methylpropiophenone (CAS: 5337-93-9)
- Chemical Structure: In this compound, there is an additional methyl group attached to the molecular structure of Methylpropiophenone.
- Applications: The presence of the extra methyl group can alter the compound’s solubility, melting point, and reactivity. It finds applications in various industrial processes, contributing to the synthesis of specialty chemicals.
5.4 General Observations:
- Reactivity: The positioning of bromine and the additional methyl group influence the reactivity of these compounds, making each suitable for specific reactions.
- Applications: While all three compounds are involved in chemical synthesis, they may find preferential use in different industries based on their unique properties.
- Availability: These compounds may be available from chemical suppliers and can be purchased for research and industrial purposes.
In summary, the distinctions in the molecular structures of 2-bromo-4-methylpropiophenone, 2 Bromo 3 Methylpropiophenone, and 4’-Methylpropiophenone result in variations in their chemical behaviors and applications. Researchers and industrial professionals choose these compounds based on their specific needs and the desired outcomes in various synthetic processes.






Leave A Comment
You must be <a href="https://jhchemco.com/wp-login.php?redirect_to=https%3A%2F%2Fjhchemco.com%2Fmethylpropiophenone-and-its-derivatives%2F">logged in</a> to post a comment.